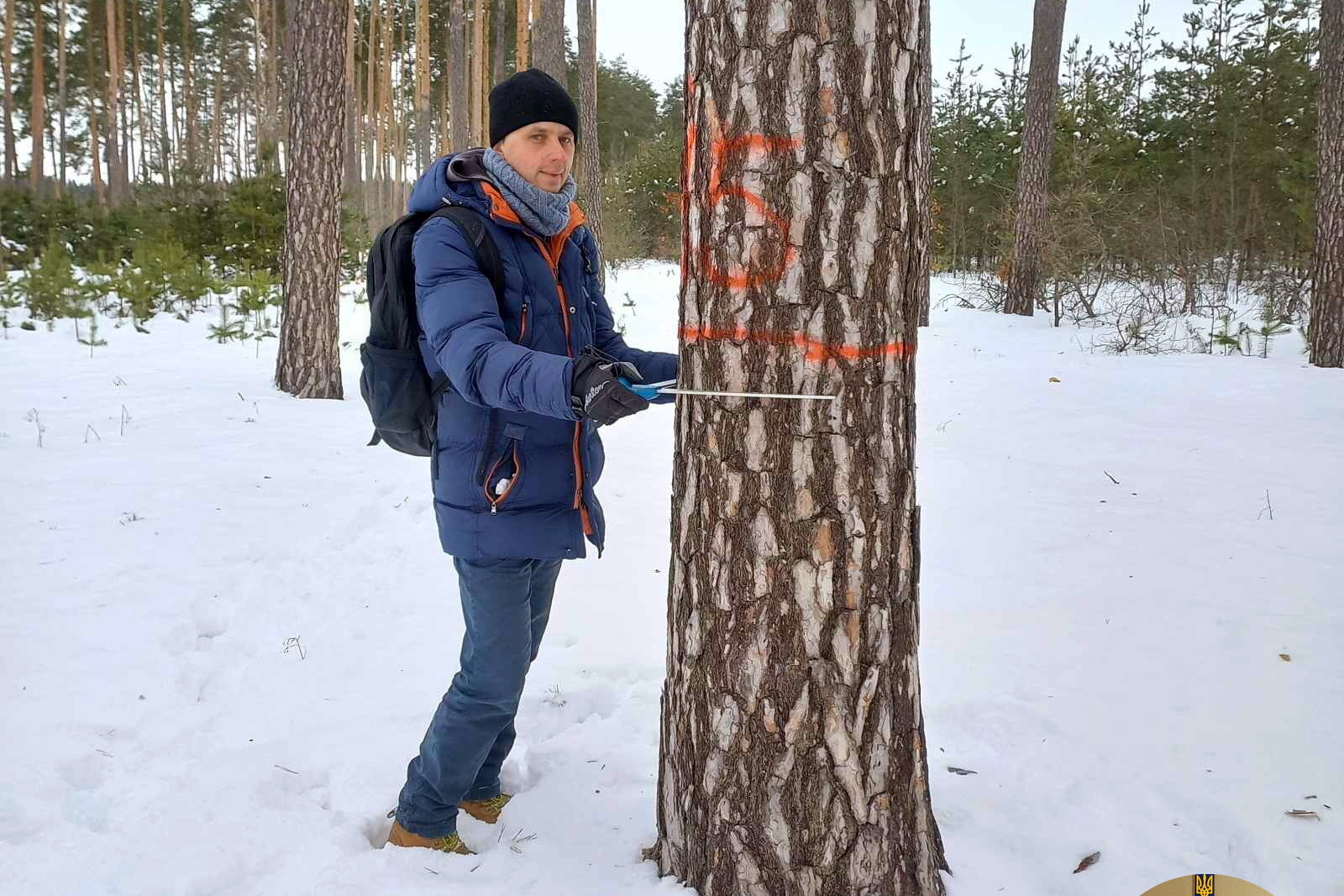
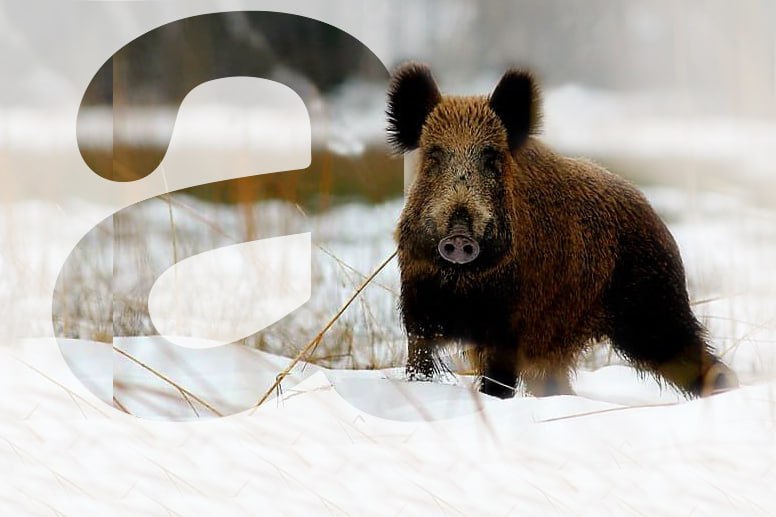
UKRAINIAN ORDER "SIGN OF HONOUR"
The institute is subordinate to the State Forest Resources Agency of Ukraine

UKRAINIAN ORDER "SIGN OF HONOUR"
RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF FORESTRY AND FOREST MELIORATION
NAMED AFTER G. M. VYSOTSKY
The institute is subordinate to the State Forest Resources Agency of Ukraine
and the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine

UKRAINIAN ORDER "SIGN OF HONOUR"
RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF FORESTRY AND FOREST MELIORATION
NAMED AFTER G. M. VYSOTSKY
The institute is subordinate to the State Forest Resources Agency of Ukraine
and the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine